The most well-liked smartphones provide a wide range of RAM capacities. Ultra-premium devices with up to 12GB or 16GB of RAM are available at one end of the spectrum. Budget phones, however, come in models with only 4GB of RAM. In the meantime, there are a ton of gadgets with 6GB and frequently 8GB of RAM in the middle ground. Less priced phones often have less RAM, whereas high-end, premium flagships provide substantially more.
Your smartphone and every other computer make use of Random Access Memory (RAM). The OS, the apps you have open, and their data are all saved in RAM while the machine is in use. Many high-end gadgets had 3GB of RAM in past. Then 4GB became the industry standard a few years later. Today, 4GB is thought to be the absolute minimum for a new device.
Any amount of RAM on your device is a limited resource that needs to be controlled. Every time you launch a new app, a percentage of this memory must be used by it. While more complex games may require up to a gigabit of RAM, simpler programs and games will only take a few hundred megabytes.
It seems clear that 4GB will not be enough for regular multitasking. Six gigabytes of RAM will cure this issue. The Galaxy S21 Ultra’s 12GB memory is incredibly capable and efficiently used. At least 15 games, some of which are rather demanding, as well as a few internet tabs, can run simultaneously in RAM.
Based on these results, our effort is to find a way to increase the RAM of your smartphone if it is already insufficient. Now let’s ask what measures can be taken for that.
How RAM is Used in Modern Smartphones
virtual components “Dummy files” are present on modern gadgets. They are produced during startup and contain extra info (battery level, processor speed data). There is always space in RAM for these components, which can be found in the /proc directory.
visual processor. The phone needs memory in order for the graphics chip to operate properly (VRAM). Additionally, as embedded GPUs lack a dedicated VRAM, they make use of the “operating system.”
Core. The Linux kernel, which powers Android-based devices, is kept in a file that is retrieved from the phone’s operating memory while it is running. As a result, allotted memory enables the kernel and its modules, hardware-controlled drivers, and caching of data inside and outside the kernel.
Information and communication. The required information on the product code and other device identification codes is kept in a different memory section. NVRAM. Once the phone is turned off, it does not erase this non-volatile memory. When the device is powered on, the modem must be able to handle the software that transfers this data to RAM.
The memory, which is utilized to run and carry out applications, is only remained in the mobile device after these procedures.
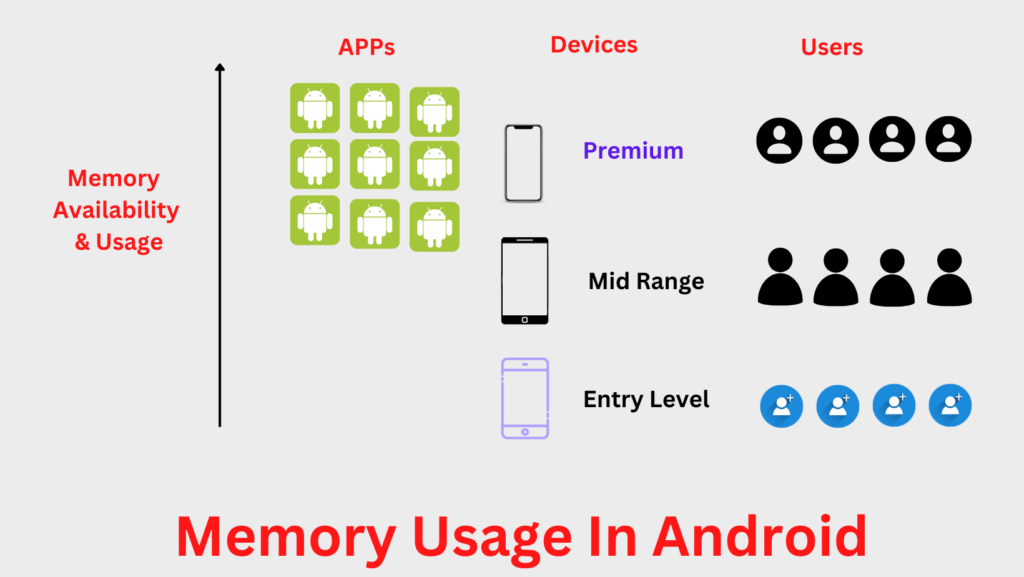
An explanation of memory management
Modern computers use a process called swapping to deal with this possibility. What it does is, the oldest and least used memory pages are released from RAM and written to swap storage. Stored memory pages are read from cache and copied back to RAM if swapped-in memory is needed later. This significantly increases the amount of memory that can be used to store applications and data, but it is slower than RAM.
Android uses a slightly different method. Android compresses the data and writes it back to RAM rather than paging it into storage. Following the Unix/Linux convention of using the letter “z” to denote compression, this is called zRAM.
Swap space, especially zRAM, is a scarce resource. Android should start deleting existing apps from memory if it runs out of swap space. Because Android wants to create enough space for the new app you want to launch, you may be forced to close an app you plan to return. All of this suggests that the more RAM you have, the more programs Android will kill without the old apps running at once.
Utilizing apps to Increase RAM on Android
There is another crucial aspect to consider when discussing whether the RAM can be increased. It is a truth that some programs actively use RAM even though they are not displayed in the list of current programs. It might not be essential to increase the so-called “operational memory” if they are disabled or eliminated. In this scenario, RAM is increased as follows:
- Go to settings.
- Select “functioning utilities” (RAM using programs in that moment)
- Click the “Stop” button after choosing any of the programs.
After performing the aforementioned actions, the utility will stop until it is used again. The smartphone will respond to user commands more quickly thanks to this effective RAM-saving technique.
Memory cleanup manually
It is advised to start by attempting to manually boost Android’s free RAM. Since cellphones lack the ability to install additional cards, as is the case with PCs, RAM optimization is required. Closing useless programs is done at the expense of “operational memory” cleaning. The process for doing this is as follows:
- Launch the list of currently executing programs.
- To close all open applications, press the “X” or “Close All” button.
This process just needs a short amount of time. It is advised to carry it out frequently without having dozens of programs running.
Utilizing third-party software
The desired outcome is not always achieved via manual optimization. Therefore, the option to try clearing Android RAM using third-party applications is provided to the user. Unnecessary objects can currently be removed using a number of the utilities that are currently offered in the official Play Market store.
Among the top programs are the following ones:
Using third-party programs
Manual optimization does not always give the desired result. Therefore, the user is offered the opportunity to try cleaning Android RAM with third-party software. To date, there are quite a few utilities available in the official Play Market store that allow you to remove unnecessary items.
The following programs are among the leaders:
- Phone Cleaner.
- CCleaner.
- Clean Master.
- OneBooster.
- Swapper – ROOT (Free)
- Free Swapper for Root (Free)
- AMemoryBoost (Swap enabler) (Free)
All these apps function in the same way:
- Start the app.
- Establish a swap file.
- Set the required swap file’s size.
- Decide where to put the swap file (external microSD card or internal storage)
- Await the creation of the swap file.
- After finishing, you might need to restart your phone so that the swap file can initialize.
Keep in mind to keep the software installed as long as you need the swap file to function.
Basically Increase RAM on an Android Phone or Tablet
There are three primary parts of employing the swap file approach to increase RAM on Android:
- An excellent microSD card (highest capacity needed)
- An Android device with root access
- A program for controlling the swap file
Although rooting Android is simple, it might not be sufficient. Some smartphones (like the Xiaomi Redmi Note 4) have a kernel-level swap file size restriction. Therefore, no quantity of rooting and swap file administration will increase your Android’s RAM larger. Use a checking software to quickly determine whether you can manually boost Android RAM. Swap file Check and Memory-Info are two decent examples.
To start testing, simply launch the application and select Start RAM Expander Test Here. The software will display a message that says “Congratulations” and the maximum increase if enlarging the swap file is possible. You’ll see that this is a helpful tool that also provides a list of RAM and storage information.
To increase RAM in this way, get a quality SD card
Consider using the microSD card in your phone if the swap file on your tablet or phone can be modified. This card must be quick and durable, as was already mentioned. Avoid purchasing any old microSD card. Instead, invest a bit more money on more durable storage, which will increase reliability. When purchasing a new microSD card, look at the rating on the box. Class 4 is the lowest suggested rating, and Class 10 is the best.
Warning: Adding more RAM to your Android device using an SD card will shorten the life of the media. It is significant to keep in mind that some phones forbid using external storage (your microSD card) as a swap file. However, if your phone has enough internal storage, you can use that instead, though it might have a shorter lifespan.
Recommended :
Factory Reset A Samsung Tablet
Frequently Asked Questions :
01) How can I see the free RAM?
To begin with, you must activate developer mode. To accomplish this, select “About phone” from the device’s settings, and then press the build number 5-7 times. Next, you must select the “Memory” tab under “For developers.” Using the standard search function in the smartphone settings is the quickest approach to discover the required tab.
02) Exists a way to entirely free up RAM space?
Yes, but only after you switch off your smartphone. In this situation, it’s important to keep in mind that when the device is turned on again, the “RAM” will automatically start to fill. And this occurs as a result of the software’s initial operation.