CentOS is a free software initiative that produces CentOS Stream and CentOS Linux, two separate Linux® versions. The source development environment for upcoming Red Hat® Enterprise Linux product versions is Stream.
Between 2021 and 2024, the CentOS Project will stop producing updates and new versions of Linux® version. As a result, existing Linux users will have to decide how to migrate. CentOS Linux 7 updates will stop on June 30, 2024, and CentOS Linux 8 updates ceased in December 2021.
The naming scheme used by CentOS
Community Enterprise Operating System is what the acronym stands for. It is an acronym that appears in the identities of two Linux distributions. Those are numerous work units, and the open software community.
Comparison of Linux and Stream Versions
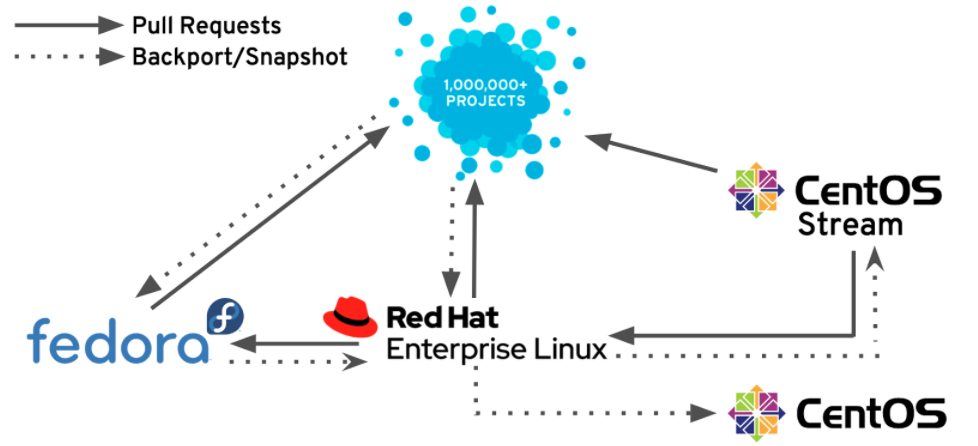
Both are components of the larger enterprise Linux ecosystem and open source Linux distributions that are variations of CentOS. The open-source development environment for upcoming Red Hat Enterprise Linux releases is Stream.
Red Hat is the source code for Linux version. The Stream version is what will eventually constitute Red Hat Enterprise Linux.
Each major version of Red Hat Enterprise Linux, which used the RPM package manager approach and maintained a similar degree of functionality, compliance, and bug patches was historically mirrored in each major version of Linux.
Stream version continually give Red Hat Enterprise Linux minor releases’ source code. It is which follows closely behind Red Hat Enterprise Linux releases.
To enable community members to contribute to and test code alongside Red Hat Enterprise Linux engineers, CentOS Stream makes Red Hat Enterprise Linux development source code accessible.
Its users can download, modify, submit patches, and suggest improvements that might be incorporated into the upcoming minor version of Red Hat Enterprise Linux, along with Red Hat partners and ecosystem developers.
Developers frequently use Red Hat Enterprise Linux for development and deployment. It is a forerunner of Linux, which lacks a contribution mechanism. Linux version updates will stop between 2021 and 2024.
The Red Hat Enterprise Linux open source development cycle, which includes the Fedora project, is as follows:
- Future major releases of Red Hat Enterprise Linux will be based on the upstream project Fedora.
- A sneak peek at forthcoming Red Hat Enterprise Linux minor versions is available in Stream.
- The authoritative, secure, and fully supported enterprise operating system is Red Hat Enterprise Linux.
- The Red Hat-derived Linux distribution CentOS, which is community-supported and -produced, will be phased out between 2021 and 2024.
Red Hat Enterprise Linux vs. CentOS
An open source project is CentOS. An enterprise open source offering is Red Hat Enterprise Linux.
There are considerable technical, support, and development differences across the three different Linux distributions, Stream, Linux, and Red Hat Enterprise Linux.
- Numerous technological variations exist, such as variations in binary execution routes.
- Utilize different support systems. Courtesy of other users and contributors give support for Stream and Linux . Engineers and personnel employ full-time to provide Red Hat Enterprise Linux support.
- They all invite, test, and commit source code changes in unique ways. Contributions to Red Hat Enterprise Linux are routed through Stream version. Anybody can suggest for the contributions to the Stream, but only Red Hat engineers can approve and commit contributions. There isn’t a contribution model for Linux.
Does CentOS have a future?
Between 2021 and 2024, the CentOS Project will stop producing updates and new versions of Linux®. As a result, existing Linux users will have to decide how to migrate. Linux 7 updates will stop on June 30, 2024, and Linux 8 updates will stop in December 2021.
The CentOS community, though, is still active. As part of the Stream project, which will continue to play a significant role in the Red Hat Enterprise Linux development cycle, community contributors and CentOS users will continue to work together on open source Linux distributions.
Based on the guidance of each group’s members and organizing leaders, CentOS SIGs will continue their work within the community.
Anyone may request permission from the CentOS governing board to launch a new SIG.
Red Hat Enterprise Linux minor releases will continue to use CentOS Stream
It is because their primary development pipeline and open source development platform.
The Red Hat Enterprise Linux 8 lifecycle’s full support phase will include updates for CentOS Stream 8, which is a component of the Red Hat Enterprise Linux 8 development cycle.
As part of the Red Hat Enterprise Linux 9 development cycle, Stream 9 was released in 2021 with a comparable update cycle.
Builds of Linux 8 will stop in December 2021, although the public will still have access to the source code at git.centos.org.
Red Hat and CentOS maintain no engagement in these initiatives, therefore companies and communities offering operating systems that are similar to Linux—such as Rocky Linux, Amazon Linux 2, Docker, and AlmaLinux—will need to be consulted directly. Gregory Kurtzer, a co-founder of CentOS, launched Rocky Linux, and he will continue to develop Linux-like distributions. The CentOS governing board chose the following timeline for the end of life of Linux:
Through June 2024, Linux 7 updates will coexist with Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7 support lifetime.
Updates for Linux 8 terminated on December 31, 2021.
Is Red Hat Enterprise Linux available without cost?
Yes. There are various initiatives that offer cost-free Red Hat Enterprise Linux subscriptions to eligible people and organizations (depending on certain variables). Both the resulting deployment and the Red Hat tooling required to support the migration are available and fully supported.
Red Hat Developer subscriptions are available for free to individual developers.
Customers of Red Hat may be eligible for a free Red Hat Developer subscription for teams.
A free Red Hat Open Source Infrastructure program may be available to open source initiatives, communities, and other nonprofit software organizations.
Through the Red Hat Academic Program, academic institutions and non-profit research institutions may be able to use Red Hat Enterprise Linux at a discounted price.
Use CentOS Stream now
A continually delivered distribution that behind Red Hat Enterprise Linux by a small margin, CentOS Stream is an upstream open source development platform that enables you to create, test, and contribute to it.
CentOS Stream, an alternative to Fedora and Red Hat Enterprise Linux, permits testing of supported software and hardware prior to the official release of Red Hat Enterprise Linux and allows users to contribute to its development.
The kernel and all user space components are included in Stream version, which is also where the majority of RHEL + 1 development takes place. It allows a quicker path to market for Red Hat layered products, ISVs, IHVs, and OEMs.
Start using CentOS Stream in one of two ways.
- Use the scripts below to switch from Linux 8 to Stream 8:
[root@centos ~]# dnf swap centos-linux-repos centos-stream-repos [root@centos ~]# dnf distro-sync
- Download CentOS Stream
FAQs
What is CentOS Linux?
Anyone who wants to use it can do so using the free and open source computing platform provided by CentOS Linux. Publicly accessible open source code that Red Hat, Inc. released for Red Hat Enterprise Linux use to create Linux.
How long after Red Hat publishes a fix does it take for CentOS to publish a fix?
Individual RPM packages are intended to be accessible on the mirrors within 72 hours of release; however, they are typically accessible within 24 hours. From time to time, packages are delayed for a variety of factors.
How do I get Updates?
Yum (in Linux 7) and dnf (in Linux 8 and Stream) are the update and package installation tools included with CentOS.
What is special about CentOS?
The software used by CentOS is very reliable (and frequently more developed), and due of the longer release cycle, applications do not require as frequent updates.
