Cybersecurity is the defense against cyberthreats for systems connected to the internet, including their hardware, software, and information. Individuals and businesses use this technique to prevent illegal access to data centers and other digital systems.
A solid cybersecurity plan can offer a strong security posture to malicious activities intended to gain access, change, remove, ruin, or extract sensitive data and systems belonging to a business or user. Security measures are essential in order to prevent attacks that try to take down or impair the functionality of a system or a device.
Importance of Cybersecurity
The importance of cybersecurity is undoubtedly going to increase as there are more people, devices, and applications in the modern company, along with an influx of more data, most of it sensitive or confidential. The increase in the quantity and degree of expertise of cyber attackers and attack approaches made this issue even worse.
Elements of Cyber Security
There are number of distinct parts in the field of cybersecurity, and it is essential for an coordination of organization within that field to have a successful cybersecurity program.
The following is a list of these parts:
- Security for applications
- Security of information or data
- Network protection
- Planning for business continuity and disaster recovery
- Operational protection
- Cloud security
- Security for vital infrastructure
- Physical security
- Client education
How Does the Cybersecurity Work?
For many businesses, maintaining cybersecurity in an ever-changing threat environment is challenging. Traditional reactive strategies, which focused their resources on defending systems against the most important known threats, while leaving lesser threats unprotected, is no longer an effective method.
To keep up with shifting security dangers, there is a need of approach that is more proactive and adaptable. Several leading cybersecurity advisory bodies provide advice.
For instance, as component of a framework for risk assessment, the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) advises implementing regular inspections and real-time evaluations to protect against both known and unidentified threats.
Advantages
The advantages of putting cybersecurity procedures into place and sustaining them include:
- Protection for businesses from cyberattacks and data leaks
- Network and data protection
- Prevent access by unauthorized users
- Quicker recovery from a violation
- End User and Endpoint Security
- Policy Compliance
- Business Continuity
- Increased trust from stakeholders, customers, collaborators, developers, and workers who works for the reputation of the company
Various Types of Treats
It can be difficult to cope up with emerging technology, security trends, and advanced threat. Safeguard data and other assets from many types of cyberthreats is important for that.
Some examples of cyberthreats are:
Malware
A sort of harmful software known as malware allows any file or program to be used against a computer user. Worms, viruses, Trojan horses, and spyware are included.
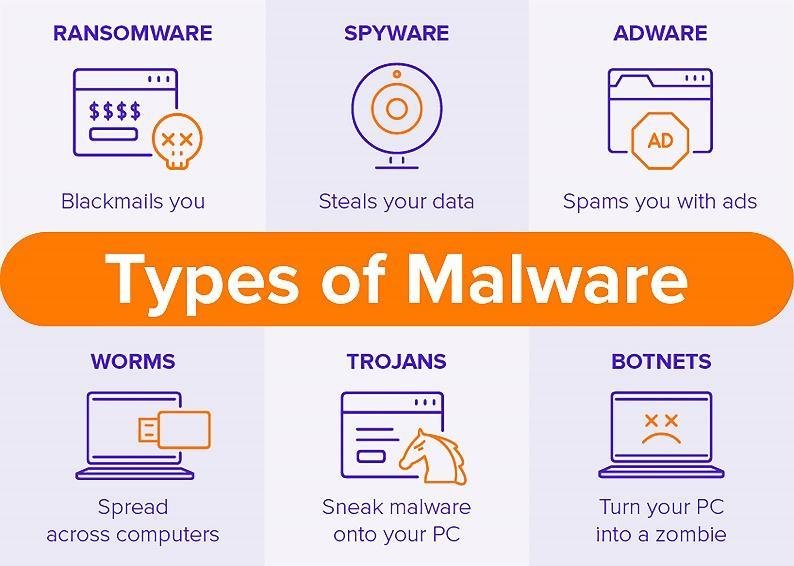
Ransomware – Malware can also include ransomware. It entails an attacker encrypting and locking the victim’s computer system files, then demanding cash to decrypt and unlock them.
Insider threats
These are security lapses or losses brought on by people, such as staff members, subcontractors, or clients. Insider dangers can be malicious or careless.
Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks
Attacks known as distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) involve several systems interfering with the operation of a targeted system, such as a server, website, or other network resource.
Attackers can slow down or disrupt a target system by flooding it with messages, connection requests, or packets, blocking legitimate traffic from accessing it.
Advanced Persistent Threats (ATPs)
Advanced persistent threats (APTs) – targeted attacks that last a long time and involve an attacker infiltrating a network and avoiding detection for a long time in order to collect data.
Social Engineering
An attack known as social engineering uses human interaction to persuade users to circumvent security measures in order to obtain typically protected sensitive information.
Phishing
Phishing is a sort of social engineering where fraudulent email or text communications that resemble those from trustworthy or known sources are sent.
Often random attacks, the purpose of such messages is to snatch sensitive data, like credit card or login details.
Spear Phishing
Spear phishing is a sort of phishing assault that has a specific target user, company or business.
Botnets, drive-by-download attacks, exploit kits, malicious advertising, vishing, credential stuffing attacks, SQL injection attacks, cross-site scripting (XSS) attacks, business email compromise (BEC), and zero-day exploits are additional frequent forms of attacks.
Major Cybersecurity Challenges
Hackers, loss of data, privacy, risk assessment and shifting cybersecurity approaches are continuous challenges in Cybersecurity. The frequency of cyberattacks is not projected to reduce in the near term.
Additionally, the emergence of the internet of things (IoT) has increased attack points of entry, necessitating a greater requirement for network and device security. Major problematic aspects of cybersecurity is the emerging nature of security risks.
New attack vectors are created as a result of the advent of new technologies and their use in novel or unconventional ways. Trying to keep up with these frequent changes and developments in attacks, and also updating procedures to defend against them, can be difficult.
Concerns include guaranteeing all components of cybersecurity are updated regularly to protect against possible risks. This can be extremely hard for smaller firms without the workforce or in-house facilities.
Additionally, businesses have access to a large amount of personal data who are using several of their amenities. With many more data being gathered, the probability of a hacker group who wants to take away personally identifiable information (PII) is also another concern.
End-user education should be a part of cybersecurity measures, as staff members may unintentionally introduce malware onto the premises on their laptops or mobile devices.
Employees who regularly receive security awareness training can help protect their firm from cyberthreats. Lack of qualified cybersecurity staff is another issue facing cybersecurity.
Businesses need cybersecurity employees to assess, monitor, and respond to problems as the amount of data they gather and utilize expands. The shortage of security experts in the workforce, according to (ISC)2, is projected at 3.1 million. For insights into fortifying cybersecurity measures, take a look here.
Automation in Cybersecurity
Automation is becoming a crucial part of keeping businesses safe from the numerous and sophisticated cyberthreats that are on the rise.
Cybersecurity can be enhanced in three key areas by utilizing artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning in sectors with high-volume data streams:
- Threat recognition – Platforms powered by AI are able to evaluate data, identify known dangers, and forecast new ones.
- Threat reaction – Platforms powered by AI can also design and automatically implement security measures.
- Human enhancement – Security professionals frequently have too many warnings and boring duties to complete.
By automating large data analysis and other repetitive operations, AI can assist reduce alert fatigue by prioritizing low-risk warnings automatically and freeing up human labor for more complex tasks.
Automation in cybersecurity also helps with intrusion and malware categorization, traffic and compliance assessment, and much more.
Vendors and Tools
Cybersecurity vendors frequently provide a range of security goods and services. Typical security devices and platforms include:
- Identification and access control (IAM)
- Firewalls
- Endpoint security
- Antimalware
- Systems for preventing and detecting intrusions (IPS/IDS)
- prevention of data loss (DLP)
- detection and response at the endpoint
- Event management and security data (SIEM)
- tools for encryption
- scans for vulnerabilities
- Internet-based private networks (VPNs)
- Platform for protecting cloud-based work (CWPP)
- Broker for cloud access security (CASB)
- Check Point, Cisco, Code42, CrowdStrike, FireEye, Fortinet, IBM, Imperva, KnowBe4, McAfee, Microsoft, Palo Alto Networks, Rapid7, Splunk, Symantec, Trend Micro, and Trustwave are a few well-known cybersecurity providers.
Carrier Opportunities of Cybersecurity
People with cybersecurity awareness and hardware and software expertise are essential as the environment of cyberthreats expands and new dangers, such IoT risks, arise.
Security positions require IT specialists and other computer experts, including:
- The chief information security officer (CISO) is responsible for managing the IT security department’s operations and implementing the security program across the entire enterprise.
- Chief Security Office (CSO) is the executive in charge of a company’s physical security and/or cybersecurity.
- Security engineers concentrate on quality assurance within the IT infrastructure to protect firm assets from threats.
- The vital infrastructure of an organization must be organized, assessed, designed, tested, maintained, and supported by security architects.
- Penetration testers are ethical hackers who examine the security of systems, networks, and apps in search of flaws that hostile users can use against them.
- Threat hunters are the threat analysts who hunt down weaknesses and attacks with the intention of thwarting them before they compromise a corporation.
Security analysts, data security officers, cloud security architects, Security Operations Management (SOC) managers and analysts, security investigators, cryptographers, and security professionals are further professions in the field of cybersecurity.
FAQs
Are cyber security threats increasing?
Yes, threats are becoming more sophisticated, intense, diverse, and numerous. Cyber specialists report a considerable increase in external cyberattacks, particularly those sponsored by criminal organizations and foreign states.
What Is Cybersecurity?
Cybersecurity is a broad concept that covers both data security and the technological platforms in charge of transporting, storing, and authenticating data.
What’s one of the biggest cybersecurity challenges businesses face?
It includes continuing your education in cybersecurity and keeping up with the latest cyberthreats. Hackers most frequently start cyberattacks after figuring out a means to get employee login information. We use the word “steal” loosely because hackers frequently trick users into giving their information to them.
What types of businesses are most at risk for a cyberattack?
You might believe that larger companies with more terminals are more susceptible than smaller companies. Or organizations with valuable data, like those in the financial services sector would be simple targets. It’s not always the case like that. Small and medium-sized firms, on the other hand, are simple targets for hackers because they lack specialized IT knowledge and cybersecurity technologies.
Is cybersecurity a good career?
In the realm of cybersecurity, unfilled positions frequently outnumber competent applicants. According to Cyber Seek, there are more than 500,000 cybersecurity job openings in the US as of this writing.
